Internet connection problems? DNS cache corrupted? Facing DNS issues or problems? Maybe you need to flush Windows DNS Cache. If your computer finds it difficult to reach a certain website or server, the problem may be due to a corrupt local DNS cache. Sometimes bad results are cached, maybe due to DNS Cache Poisoning and Spoofing, and therefore need to be cleared from the cache to allow your Windows computer to communicate with the host correctly.
Typically, there are three types of caches in Windows that you can flush easily:
- Memory Cache
- DNS Cache
- Thumbnails Cache
Clearing the Memory Cache can free up some system memory while clearing the Thumbnail Cache can free up space in your hard disk. Clearing the DNS Cache can fix your internet connection problem. Here’s how you can flush the DNS cache in Windows 11, Windows 10, Windows 8 or Windows 7.
Flush DNS Cache in Windows 11/10
To flush the DNS Cache in Windows 11/10 you need to:
- Open an administrative command prompt window as an administrator
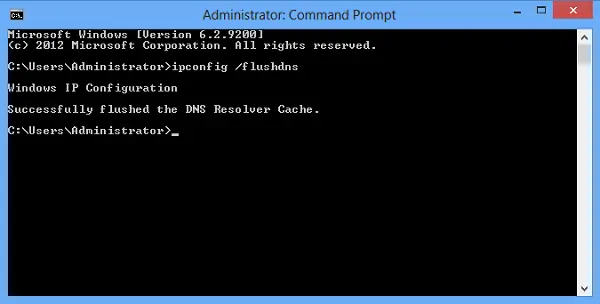
- Type ipconfig /flushdns and hit Enter
- You should see – Windows IP Configuration. Successfully flushed the DNS Resolver Cache
- Exit CMD
- Your DNS cache should have been reset.
Let us see it in a bit more detail.
You need to open an administrative command prompt window. In search box, type cmd. Then, right-click on it and choose ‘Run as administrator’ option. Alternatively, you can also open an elevated command prompt from the WinX menu.
Next, type the following and hit enter:
ipconfig /flushdnsYou should be able to see a confirmation dialog window:
Windows IP Configuration. Successfully flushed the DNS Resolver Cache.
Once the requisite process is complete and existing cache data has been flushed, you may execute the command mentioned below:
ipconfig /registerdns
This step is to register any DNS records that you or some programs may have recorded in your Hosts file.
How to flush DNS Cache using PowerShell
To flush DNS Cache using PowerShell, run PowerShell as administrator and execute the following command:
Clear-DnsClientCache
Flush DNS cache with a click using FixWin
Our freeware FixWin for Windows, let you flush the DNS cache, etc., in a click.
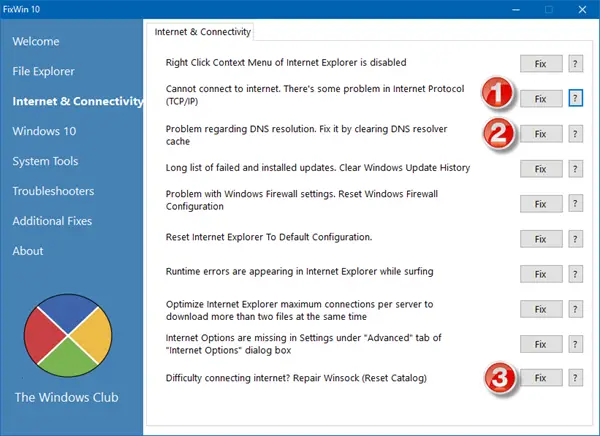
Read: How to clear or flush Google Chrome DNS Cache
How to refresh DNS cache every few hours automatically?
Take a backup of your registry before making any changes.
Open Run prompt, type regedit, and press the Enter key
This will open Registry Editor
Navigate to:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\DNSCache\Parameters
Right-click on an empty area, and create a new DWORD.
Set the Name as MaxCacheTtl and set the value in seconds. The default is 86400 seconds which is one day.
Repeat the same and create another DWORD with the name MaxNegativeCacheTtl and value as 5
This will make sure the local DNS cache is refreshed every few hours.
How to display DNS Cache
If you wish to confirm if the DNS cache has been cleared, you can type the following command and hit Enter:
ipconfig /displaydns
This will display the DNS cache entries if any.
How to Turn Off or Turn On DNS Cache
To turn off DNS caching for a particular session, type net stop dnscache and hit Enter.
To turn on DNS caching, type net start dnscache and hit Enter.
Of course, when you restart the computer, the DNC caching will, in any case, be turned on.
NOTE: Here’s a Batch File to Release TCP/IP, Flush DNS, Reset Winsock, Reset Proxy all at once.
How to Disable DNS Cache
If for some reason you wish to disable DNS caching, type services in start search and hit Enter to open the Services Manager. Here locate the DNS Client service.
The DNS Client service (dnscache) caches Domain Name System (DNS) names and registers the full computer name for this computer. If the service is stopped, DNS names will continue to be resolved. However, the results of DNS name queries will not be cached and the computer’s name will not be registered. If the service is disabled, any services that explicitly depend on it will fail to start.
Double-click on it to open its Properties box. Here change its startup type from Manual to Disabled. If you disable the DNS Client service, DNS Lookups may take longer.
These resources may also interest you: