Windows 11/10 has a Memory Diagnostic Tool that you can use to check for possible memory problems, including testing the Random Access Memory (RAM) on your computer. The tool helps you figure out bad memory, memory issues, and usually takes 20 minutes to complete.
How to run Windows Memory Diagnostics Tool
If Windows 11/10/8/7/Vista detects a possible memory problem, you will receive a notification. Click the notification to open it. If you wish to run Windows Memory Diagnostics Tool on-demand, do the following:
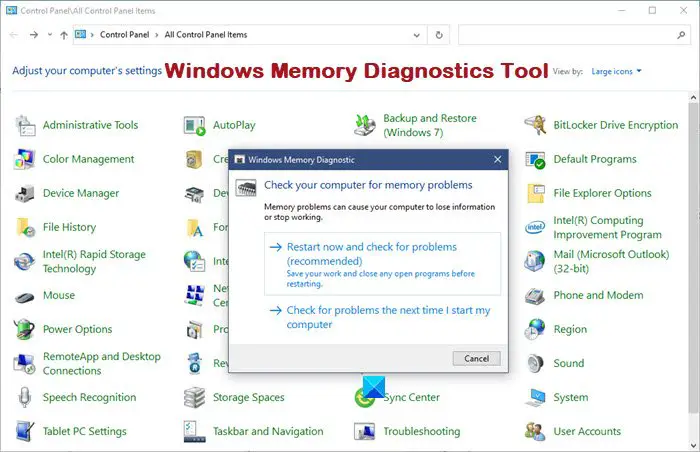
- Open Control Panel and type ‘memory‘ in the search bar. Click on ‘Diagnose computer memory problems’ to open it.
- Alternatively, you can also type ‘mdsched‘ in Start search and hit Enter to open it.
- Choose between two options for when to run the Memory Diagnostics Tool.
- You can Restart now and check for problems.
- Or you can select Check for problems the next time I start my computer.
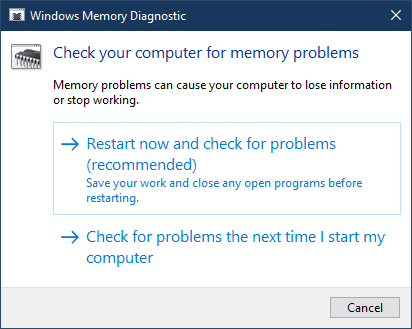
If you choose to restart your computer and run the tool immediately, make sure that you save your work and close all of your running programs. The Memory Diagnostics Tool will run automatically when you restart Windows.
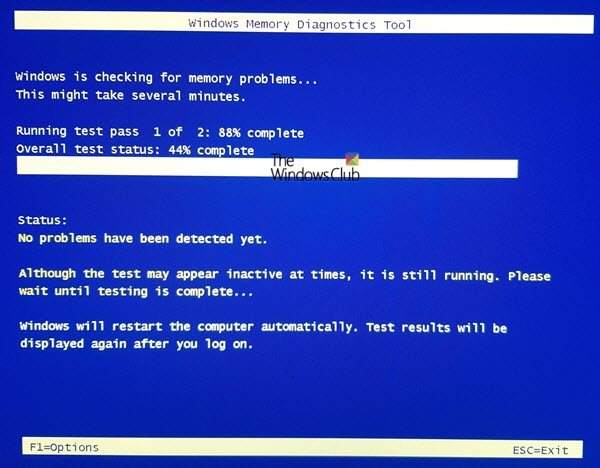
Two Test Passes will be run.
Advanced options for running the Memory Diagnostics Tool:
For most users, letting the Memory Diagnostics Tool run automatically is the recommended option. However, advanced users might want to adjust the tool’s settings. When the Memory Diagnostics Tool starts, press F1.
You can adjust the following settings:
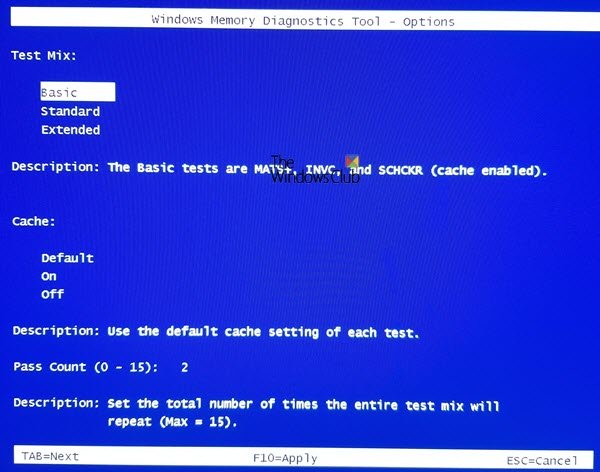
- Test mix. Choose what type of test you want to run: Basic, Standard, or Extended. The choices are described in the tool.
- Cache. Choose the cache setting you want for each test: Default, On, or Off.
- Pass count. Type the number of times you want to repeat the test.
The default is Standard, and it includes all the Basic tests, plus LRAND, Stride6, WMATS+, WINVC, etc.
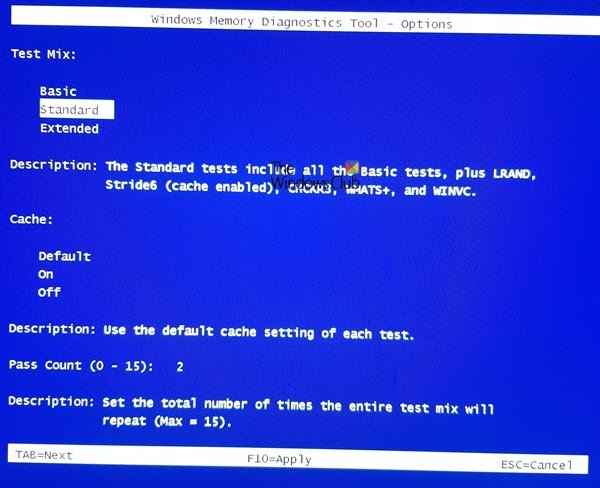
The Basic test covers MATS+, INVC, and SCHCKR.
The Advanced test includes all Basic and Standard tests plus Stride38, WSCHKA, WStride-6, CHCKR4, WCHCKR3, ERAND, Stride6, CHCKR8, etc.
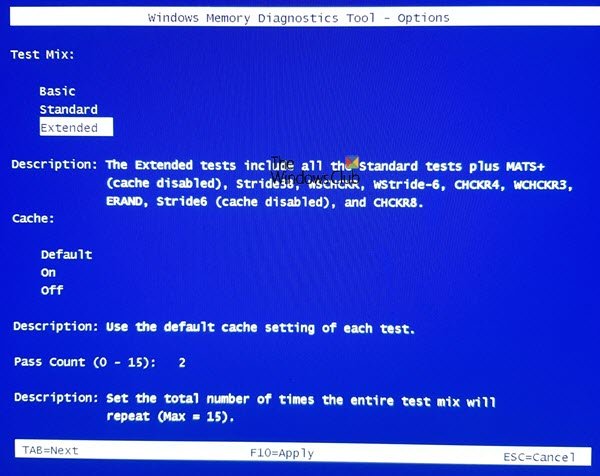
If you change your options, press F10 to save and start the test.
Else you may press Esc to continue running the default test.
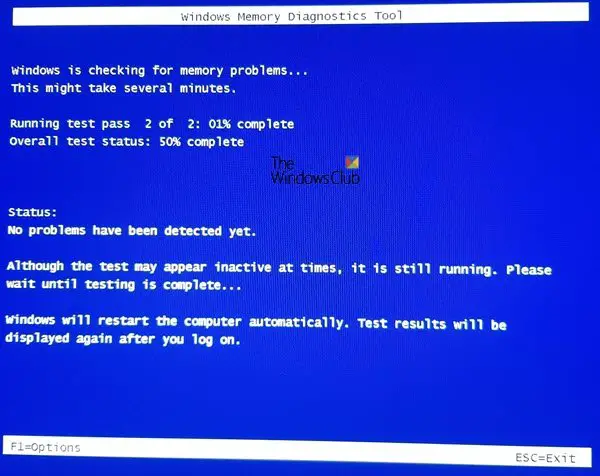
It might take several minutes for the tool to finish checking your computer’s memory.
Read: Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool stuck?
Once the test is completed, Windows will restart automatically. If the tool detects errors, you should contact your computer manufacturer for information about fixing them since memory errors usually indicate a problem with the memory chips in your computer or other hardware problem.
You may also want to try some Advanced Memory Diagnostic on Windows, with Memtest86+, and maybe check out some more PC Stress Test free software.
Is Windows Memory Diagnostic tool any good?
It’s an excellent program and a free tool to check if there is anything wrong with your RAM. If the tool shows any symptom of an issue, then you can further check with another program. Along with the standard checking tool, it also offers checks such as ERAND, Stride6, CHCKR8 to find problems with the installed RAM.
Read: How to run System Diagnostics using System Information Tool?
Why does Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool take so long?
It doesn’t perform one test and gives a result. Instead, it checks using multiple programs, and if there is a problem, you will know about it. Combine this with the amount of RAM, and it takes even more time. This tool should be used when you have an issue with the memory, and you want to be sure before replacing it.
Read: Windows Memory Diagnostic displaying no results.
Can I exit Windows Memory Diagnostic Tool?
It’s only testing the memory, and it should be fine even if you have exited in between. However, you will have to force shutdown the PC to exit the tool. I would still suggest that you better wait it out. Keep the PC plugged, and get something else done in the meantime.
Can RAM suddenly go bad?
Any hardware can go bad with time or if there is a manufacturing fault. The same applies to RAM. If everything looks good, the memory test can reveal if there is an issue with the RAM. If there is a fault, it would be best to replace it with a new RAM.
TIP: See this post if you receive Only part of a ReadProcessMemory or WriteProcessMemory request was completed message.
Very useful article
Hello,
I find an error in my pc,Could you please restore and solve my erreors
Thanks, it is helpful
What if the PC will not boot?
With the Windows 7 DVD you could run memtest, but with Win8 and Win10 DVDs there is no memory test option?
what if the next morning the PC has restarted but doesn’t show any results? Is that an indication that it had a BSOD while testing? Or how do I get to the results?
Once it restarts, you need to use the Event viewer to see the results. In Windows 10, right click the start icon, choose the third one from the top “Event viewer”. Once this opens, click Windows Logs on the left and System. Look through that and there should be an Information level with “The Windows Memory Diagnostic tested the computer’s memory and detected no errors”