The Windows Search function makes the task of finding files and folders on your Windows PC incredibly fast but sometimes the function may fail to work as desired. Many believe, this occurs mainly when Windows starts indexing files. Is it true? So, what is Windows Search Indexing and how does it affect the Search function?
What is Seach Indexing in Windows 11/10
In Windows OS, the process of looking at files, email messages, and other content on your PC and cataloging their information, such as the words and metadata in them, is termed Indexing. Indexing the contents stored on your PC helps you get results faster by looking at an index of terms. Initially, when the Indexing process runs, the process can take up to a couple of hours to complete. Thereafter, it silently runs in the background of your PC and simply re-indexes updated data. Let us take a look at the following aspects:
- How does indexing affect Search in Windows 10?
- Types of files that can be indexed
- How much of a file’s information is indexed?
- How much space is used by the index?
- Where is the index information stored?
- Why does indexing always run on a PC?
1] How does indexing affect Search in Windows 11/10
Much like an index of a book, a well-made digital index can help quickly direct the user to the information he is looking for by scanning for common properties. Besides, it will return with the most valid results in seconds. In the absence of Indexing, the process could take minutes, for the same operation to complete. Thus, Indexing speeds up the search results!
On the other hand, many apps in the Microsoft Store too, depending on the index to provide up-to-date search results for your files and other content. Disabling indexing for Microsoft Store may result in the apps running either slowly or not working at all. It depends on how heavily these apps rely on the Indexing feature.
Choosing not to index the contents of files can reduce the size of the index. However, it may make the process of finding files harder.
Related: SearchIndexer.exe is preventing this device from being stopped
2] Types of files that can be indexed
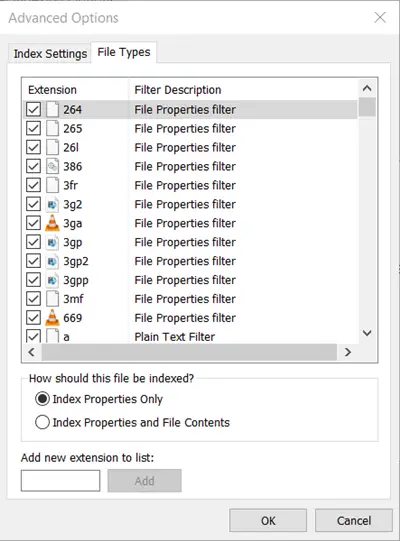
In addition to files bearing names, files showing some properties or metadata present in some binary format such as DOC or PDF can be indexed. The ‘File Types‘ tab of ‘Advanced Indexing Options‘ can be used to include or exclude certain file types from search and their contents and properties. To see how it is done, see our post on Windows Search Indexer and Indexing Tips & Tricks.
Also, apps you choose to install to your PC can add their own information to the index to speed up searching. Services such as Outlook adds all emails synced to a machine to the index by default. It uses the same index for searching within the app.
All the properties of your files, including file names and full file paths, are indexed, by default.
3] How much of a file’s information is indexed?
There are two ways via which you can decide how much of a file can be indexed –
- Properties only
- Properties and content
For the former, indexing will not look at the contents of the file. It will just allow searching by file name.
4] How much space is used by the index?
The indexing process can take up available space if there are lots of files that are small in size. The index size will increase dramatically in proportion to the size of the files.
Under a usual scenario, the index will be less than 10% of the size of the indexed files. For example, if you have 1GB of text files, the index for those files will be less than 100 MB.
5] Where is the index information stored?
All the information or data gathered via Indexing is stored locally on your PC at the following location:
C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\Search
If required you can change the location of the Windows Search Index.
None of the information is sent to Microsoft or outside your computer. However, apps you install on your PC can access the data in your PC’s index. It is, therefore, necessary to be careful while installing something from outside. The best thing to do is to make sure that the source is trusted.
Windows.edb is the database file of the Windows Search service, which provides content indexing, property caching, and search results for files, e-mail, and other content.
6] Why does always indexing run on a PC?
The purpose of indexing is to constantly track changes made to the files and update itself with the latest information. As such, it can open recently changed files, identify the changes made to it, if any and update the index with the latest information. But at times, the Search Indexer is reported to consume High Disk or CPU usage.
TIP: See this post if the Windows Search Indexer is not working.