Random Access Memory has a major contribution to the working of any operating system. It is a non-writable memory, unlike ROM. The increased RAM can help the operating system work smoothly. You must have noticed that initially, the system works with an accurate speed, but gradually its speed decreases, and it begins to hang up while the ongoing task is in progress. It happens because of the occupied memory of RAM by the application programs. This post will guide you on how much RAM an app is using so that you could determine which application program is consuming your memory more.
How to check how much RAM an app is using in Windows 11/10
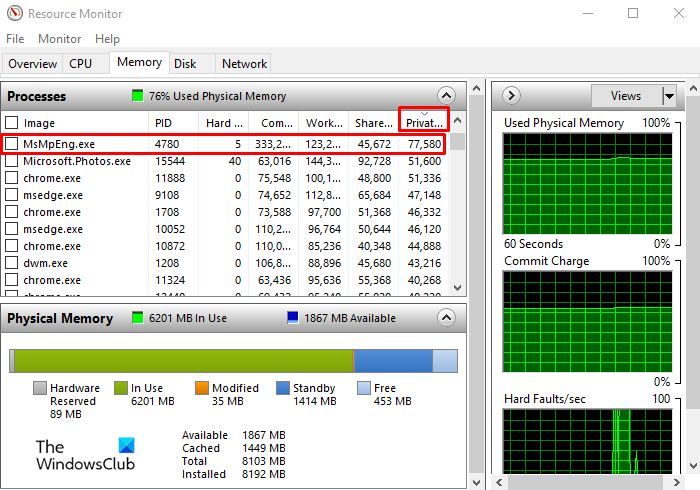
You can determine the portion of RAM used by the processor, operating system, driver, and the remaining memory available for usage. Let us know how to find out the details about the random access memory of our computer using the following suggestions:
- Open the Resource Monitor system application.
- Go to the ribbon and select the Memory tab.
- Click the Private (KB) column.
- Now, check and confirm which app is using the most memory.
You can now see the above steps in detail if it’s required.
If you want to check how much RAM an app is using, you need to open the Resource Monitor system application.
To do so, open the Windows Task Manager and switch to the Performance tab. Now go to the bottom area and click on the Open Resource Monitor link. Alternatively, simply type resmon in the Search box and hit Enter.
Inside the Resource Monitor app, go to the Memory tab and then click on the Private Kb header on the right-hand side.
The name of the programs shown in the Resource Monitor is not the same as displayed in the Task Manager. This is because the Resource Monitor uses the processor name and the Task Manager uses user-friendly names. In case of any confusion, the name of the programs can be searched on the internet for better clarity, if needed.
The Private KB will help you know which of your application programs is occupying the memory and making the operating system work slowly. In case the applications with high memory occupancy do not require the ongoing task, you can choose to end the process.
Read: How to Free up, Reduce or Limit RAM usage in Windows 11
To stop the application program, simply select the program in the resource monitor. Then right-click and select the End Process option from the context menu. This will stop the application program and will increase the available space in RAM.
That’s it. Hope you find this article helpful.
Related: What are the signs of RAM failure and how to check faulty RAM?
How to see which app is using more RAM?
To see which app is using more RAM, open Task Manager by pressing Ctrl + Shift + Esc. Navigate to the “Processes” tab, where you’ll find a list of running applications. Click on the “Memory” column to sort by RAM usage, identifying which apps are consuming the most memory effectively.
How do I allocate more RAM to a specific app in Windows?
To allocate more RAM to a specific app in Windows, open Task Manager by pressing Ctrl + Shift + Esc. Navigate to the “Details” tab, right-click the desired app, and select “Set Priority.” Choose a higher priority level like “Above Normal” or “High” to allocate additional RAM, enhancing app performance.