Ransomware has become a serious threat to the online world these days. Many software firms, universities, companies, and organizations around the world are trying to take precautionary measures to save themselves from ransomware attacks. The United States and Canadian governments have issued a joint statement about ransomware attacks urging users to stay alert and take precautions. On May 19th, the Swiss government observed the Ransomware Info Day, to spread awareness regarding ransomware and its effects. Ransomware in India too is on the rise.
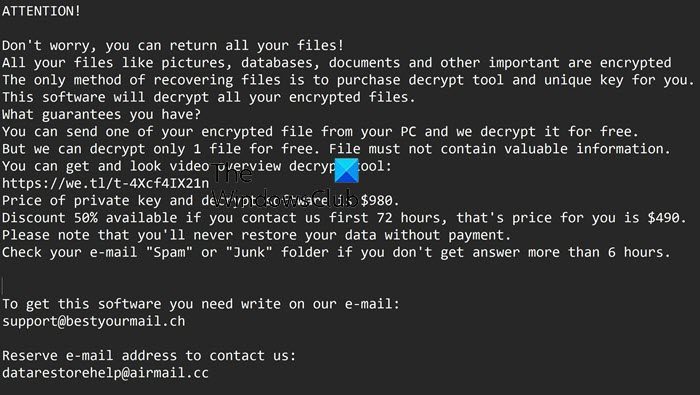
Microsoft recently published a data mentioning how many machines (users) were affected by ransomware attacks across the world. It was found that the United States was on the top of ransomware attacks; followed by Italy and Canada. Here are the top 20 countries which are majorly affected by ransomware attacks.
Here is a detailed write-up that will answer most of your questions regarding ransomware. This post will take a look at What are Ransomware Attacks, the Types of ransomware, How does ransomware gets on your computer and suggests ways of dealing with ransomware.
Ransomware attacks explained
What is Ransomware
Ransomware is a type of malware that locks your files, data or the PC itself and extorts money from you in order to provide access. This is a new way for malware writers to ‘collect funds’ for their illegitimate activities on the web.
How does ransomware get on your computer
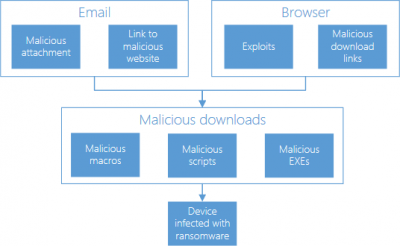
You could get ransomware if you click on a bad link or open a malicious email attachment. This image from Microsoft describes how the ransomware infection takes place.
Ransomware looks like an innocent program or a plugin or an email with a ‘clean’ looking attachment that gets installed without the user’s knowledge. As soon as it gets its access to the user’s system, it starts spreading across the system. Finally, at one point of time, the ransomware locks the system or particular files and restricts the user from accessing it. Sometimes, these files are encrypted. A ransomware writer demands a certain amount of money to provide access or decrypt the files.
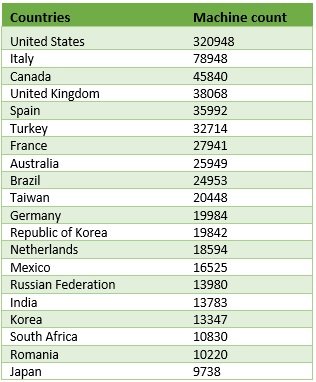
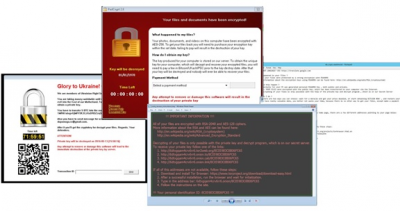
A fake warning message by a ransomware looks as follows:
However, during the ransomware attacks, there is no guarantee that the users will get back their files even after paying the ransom. Hence, it is better to prevent ransomware attacks than trying to get back your data from some way or another. You may use RanSim Ransomware Simulator to check if your computer is sufficiently protected.
Read: What to do after a Ransomware attack on your Windows computer?
How to identify ransomware attacks
The ransomware generally attacks the personal data, such as user’s pictures, documents, files, and data. It is easy to identify the ransomware. If you see a ransomware note demanding money to give access to your files, or encrypted files, renamed files, locked browser or a locked screen of your PC, you can say that ransomware has got a grip on your system.
However, the symptoms of ransomware attacks can change as per the types of ransomware.
Read: Malware Tracker Maps that let you view Cyber Attacks in real-time.
Types of ransomware attacks
Earlier, ransomware used to display a message stating that the user has done something illegal and they are being fined by the police or the government agency on the basis of some policy. To get rid of these ‘charges’ (which were definitely false charges), users were asked to pay these fines.
Nowadays, a ransomware attack in two ways. It either locks the computer screen or encrypts certain files with a password. Based on these two types, the ransomware is divided into two types:
- Lock screen ransomware
- Encryption ransomware.
Lock screen ransomware locks your system and demands a ransom for letting you access it once again. The second type, i.e. the Encryption ransomware, changes the files in your system and demands money to decrypt them again.
The other types of ransomware are:
- Master Boot Record (MBR) ransomware
- Ransomware encrypting web servers
- Android mobile device ransomware
- IoT ransomware.
Who can be affected by the ransomware attacks
It doesn’t matter where you are and what device you are using. Ransomware can attack anybody, anytime and anywhere. The ransomware attacks can take place on any mobile device, PC or laptop when you are using the internet for surfing, emailing, working, or shopping online. Once it finds a way to your mobile device or the PC, it will employ its encryption and monetization strategies into that PC and mobile device.
When can ransomware get a chance to attack
So what are the possible events when ransomware can strike?
- If you are browsing untrusted websites
- Downloading or opening file attachments received from unknown email senders (spam emails). Some of the file extensions of these attachments can be, (.ade, .adp, .ani, .bas, .bat, .chm, .cmd, .com, .cpl, .crt, .hlp, .ht, .hta, .inf, .ins, .isp, .job, .js, .jse, .lnk, .mda, .mdb, .mde, .mdz, .msc, .msi, .msp, .mst, .pcd, .reg, .scr, .sct, .shs, .url, .vb, .vbe, .vbs, .wsc, .wsf, .wsh, .exe, .pif.) And also he file types that support macros (.doc, .xls, .docm, .xlsm, .pptm, etc.)
- Installing pirated software, outdated software programs or operating systems
- Logging into a PC that is a part of the already infected network
Precautions against ransomware attacks
The only reason ransomware is created, is because the malware writers see it as an easy way to make money. Vulnerabilities such as unpatched software, outdated operating systems or people’s ignorance is beneficial for such people with malicious and criminal intentions. Hence, awareness is the best way to avoid any attacks by ransomware.
Here are are a few steps you can take to tackle or deal with ransomware attacks:
- Windows users advised keeping their Windows Operating System up-to-date. If you upgrade to Windows 10, you will reduce the events of the ransomware attack to the maximum extent.
- Always back-up your important data in an external hard-drive.
- Enable file history or system protection.
- Beware of phishing emails, spam, and check the email before clicking the malicious attachment.
- Disable the loading of macros in your Office programs.
- Disable your Remote Desktop feature whenever possible.
- Use two-factor authentication.
- Use a safe and password-protected internet connection.
- Avoid browsing websites that are often the breeding grounds for malware such as illegal download sites, adult sites and gambling sites.
- Install, use, and regularly update an antivirus solution
- Make use of some good anti-ransomware software
- Take your MongoDB security seriously to prevent your database from being hijacked by ransomware.
The Ransomware Tracker helps you track, mitigate and protect yourself from malware.
Read: Protect against and prevent Ransomware attacks.
While there are some ransomware decryptor tools available, it is advisable that you take the problem of ransomware attacks seriously. It not only endangers your data, but it can also breach your privacy to such extent that it can harm your reputation also.
Says Microsoft,
The number of enterprise victims being targeted by ransomware is increasing. The sensitive files are encrypted, and large amounts of money are demanded to restore the files. Due to the encryption of the files, it can be practically impossible to reverse-engineer the encryption or “crack” the files without the original encryption key – which only the attackers will have access to. The best advice for prevention is to ensure confidential, sensitive, or important files are securely backed up in a remote, unconnected backup or storage facility.
If you do happen to have the misfortune of being infected with ransomware, you can if you wish, report Ransomware to FBI, Police or appropriate authorities.
Now read about Ransomware protection in Windows.